When a person is actively addicted to drugs or alcohol, they are consumed with satisfying their craving for the substance. They struggle every day with their addiction without thinking about the damage they are doing to their physical and mental health. The longer a person uses substances, the higher the risk of serious and irreversible damage. Drugs, both legal and illegal, can slowly destroy a person’s vital bodily functions and systems, resulting in permanent disability or death. Some illegal drugs can cause lifelong damage even without excessive consumption.
The Effects of Addiction on Physical and Mental Health
Substance addictions are associated with many long-term physical and mental health effects. The exact effects of a drug vary depending on the following:
- The type of substance
- How often the drug was taken
- How much of the substance was taken
- The method used to take the substance
- The individual’s general health
Although the long-term effects of different drugs vary, common symptoms do occur, such as increased risk of lung disease, cardiovascular disease, stroke, cancer, infectious diseases, and addiction. The damaging effects of drugs can affect every organ in a person’s body.
Long-term Mental Health Effects of Addiction
Drugs are psychoactive substances. They all affect the brain by changing its chemistry. When a person has a substance use disorder, their chronic drug use causes changes to their brain’s structure and functions. It alters the brain’s signals, affecting how the person feels, acts, thinks, and reacts.
Long-term mental health effects of addiction include:
- Difficulty with cognitive processing, which includes all mental functions, such as memory, learning, intelligence, reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making
- Impaired information processing, such as emotional behavior and learning, motivation, and integrating emotions
- An increase in antisocial behavior
- An increase in aggressive and violent tendencies
- Mood disorders, such as depression, anxiety, paranoia, hypochondria, delusions, hallucinations, or other neurological disorders
Permanent brain damage can result from long-term drug or alcohol addiction.
Long-term Physical Health Effects of Addiction
The impact of drug or alcohol addiction is far-reaching. It can cause or worsen many physical health problems. The damage to the body can last for years and sometimes forever. Almost every organ and system in the body is affected by addiction.
The Cardiovascular System
Long-term substance addiction places a lot of stress on the cardiovascular system. Depending on the drug, heart rate and blood pressure can increase or decrease to life-threatening levels, and dangerous heart arrhythmias may occur. Cocaine, methamphetamines, and other stimulants are especially hard on the heart. They cause damage to the heart each time they are used. Addiction to stimulants can result in strokes, long-term heart disease, heart failure, and cardiac arrest. Consistent low or high blood pressure puts the person at an increased risk of circulatory problems, such as ischemic injury or blood clots. If an individual is an injection drug user, they are at risk of bacterial infections in the heart and bloodstream and collapsed veins.
The Respiratory System
Some central nervous system depressants, such as heroin and opioids, can cause breathing to be slow, irregular, or shallow. The person’s oxygen supply becomes diminished. Hypoxia can occur and lead to death. When a drug is smoked or inhaled, like crack cocaine, the person is at an increased risk of lung cancer, chronic bronchitis, pneumonia, emphysema, and infections. If the person has asthma, drugs will worsen their condition.
The Gastrointestinal System
Drug addiction can damage many areas of the gastrointestinal system, which consists of the salivary glands, mouth, esophagus, throat, stomach, gallbladder, pancreas, large and small intestine, and rectum. Drugs taken orally, such as alcohol or prescription ADHD medication and opioids, can damage the digestive system. Cocaine causes abdominal pain and damages bowel tissue. Opioids often cause abdominal pain, chronic constipation, and acid reflux. Gastrointestinal reflux disease is usually associated with alcoholism and can damage the esophagus.
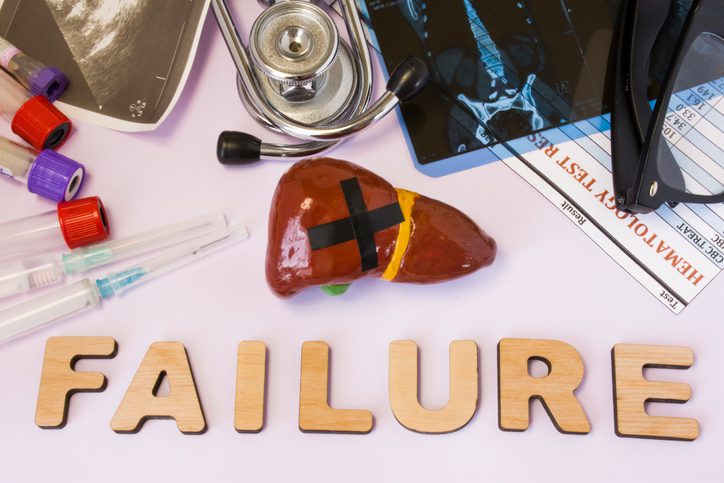
The Liver
Liver failure is usually associated with alcoholism. However, it can also be from long-term use of cocaine, methamphetamine, amphetamine-type stimulants, and cannabis. The liver clears toxins from the bloodstream and is damaged by drug use. When it is overworked, it becomes damaged and can lead to liver failure and death. Liver cancer, cirrhosis of the liver, toxic hepatitis, alcoholic hepatitis, hepatitis A, B, and C, and alcoholic fatty liver disease can all occur from chronic drug use.
The Kidneys
The kidneys act as a filter for removing toxins from the bloodstream. Every drug a person takes passes through their kidneys. The large amounts of toxins in drugs cause the kidneys to become overworked, resulting in progressive kidney damage. If renal failure occurs, the individual would require dialysis. The substances most commonly associated with renal toxicity and failure are alcohol, methamphetamine, heroin, cocaine, and morphine.
It is Never Too Late to Get Help for Addiction
Addiction is a treatable chronic disease. Are you or someone you care about struggling with addiction? If so, the sooner you get help, the less damage you will have to your mental and physical health. Our skilled professionals at Canyon Vista Recovery Center in Mesa, Arizona, can help. Contact Canyon Vista today.